In Leo Tolstoy’s great novel ‘War and Peace’, a Russian general charged with defeating Napoleon and expelling the French from Russian soil argued against rushing into battle, saying the strongest of all warriors were “time and patience”.
It’s an observation worth recalling as the media runs thousands of words analysing the causes, consequences and legacy of the global financial crisis of 2008. The 10 years since the GFC have again revealed the value of these two tried and tested techniques.
The GFC, as it’s known in Australia and New Zealand, is widely considered by economists to have been the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression.
What began as a breakdown in the US subprime mortgage market morphed into a series of credit shocks, bank crashes and a deep recession in much of the developed world. The climax of the crisis was the collapse of US investment bank Lehman Brothers in September 2008, triggering a bailout of the banking system and extraordinary fiscal and monetary stimulus by governments and central banks.
For investors, it was clearly an anxious time. Global equity markets plunged by 40% or more. By late 2008 Queen Elizabeth, whose personal fortune had fallen by more than $50 million, demanded economists explain why they hadn’t seen the crisis coming.1
At the World Economic Forum in the Swiss town of Davos in early 2009, the most popular session was one in which a panel of economic experts, many of whom had not predicted in the first place, lined up to provide their analysis of why the crisis had occurred and what would most likely happen next.
In terms of the economic analysis, there clearly was a spectrum of opinion. Some blamed lax regulations; others too much regulation. Many cited excessive debt, irresponsible lending, complex financial products, compromised ratings agencies, an over-reliance on mathematical models or just plain old greed.
But aside from a temporary seizure in short-term money markets, where banks lend to each other, global share and bond markets performed as you would expect at a time of heightened uncertainty. Prices adjusted lower as investors demanded a higher expected return for the risk of investing.
1. ‘Queen Asks Why No One Saw Credit Crunch Coming’, The Telegraph, 5 November, 2008.
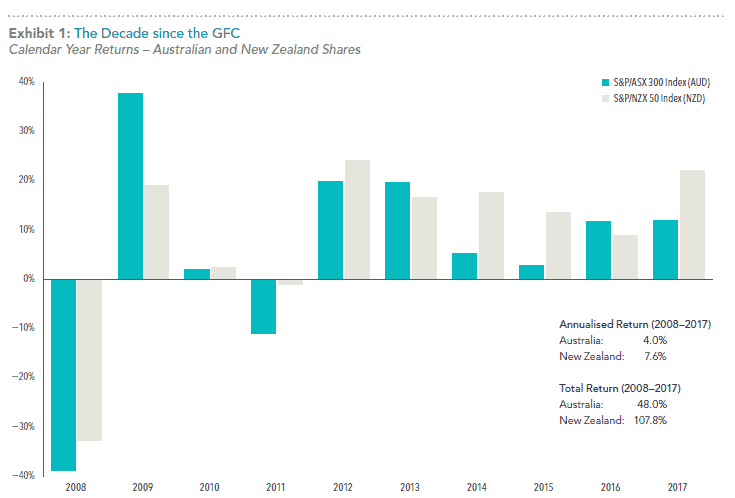
In mid-March 2009, sentiment started to turn. By the end of that year, the Australian benchmark S&P/ASX 300 Index had risen 37.6%, recovering just as dramatically from the near 39% plunge it had suffered the previous year. The New Zealand market rebounded by more than 19% after a near 34% decline in 2008.
By the end of 2017, the Australian index had delivered an annualized return of 4.0% even to someone who had begun investing just before the crisis began. Using a global balanced strategy of 60% equity and 40% fixed interest, the return was 5.2%.
By the end of the same period, an investor who had begun investing in the New Zealand market at the start of 2008 would still have experienced a 7.6% annualized return by the end of 2017. Using the same global balanced strategy, the New Zealand dollar return was 5.4%.
The lessons from this experience are familiar. Emotions are hard to keep in check during a crisis. There can be an overwhelming compulsion among investors to “do something”. But, as it turned out, those who listened to their advisors and stayed disciplined within the asset allocation designed for them have done considerably better than many people who capitulated and went to cash in 2008−2009.
Think of two people reluctantly encouraged to take a rollercoaster ride. One of them focuses on every sharp turn and sudden decline, his sense of terror compounded by the attention he is paying to the screams of those around him. The second person focuses on a static point on the horizon and tells herself the ride will soon be over.
The arguments over the causes and consequences of the GFC will go on and on. But as investors, there’s much to be said for focusing on what we can control.
Timing the market is tough, as is basing an investment strategy on economic or market forecasts. But we can do ourselves a favour, both materially and emotionally, by accepting that volatility is a normal part of investing and by sticking to a well-thought-out investment plan agreed upon in less stressful times.
Like Tolstoy’s general said, the strongest warriors are time and patience.
This advice may not be suitable to you because it contains general advice that has not been tailored to your personal circumstances. Please seek personal financial and tax/or legal advice prior to acting on this information. Before acquiring a financial product a person should obtain a Product Disclosure Statement (PDS) relating to that product and consider the contents of the PDS before making a decision about whether to acquire the product. The material contained in this document is based on information received in good faith from sources within the market, and on our understanding of legislation and Government press releases at the date of publication, which are believed to be reliable and accurate. Opinions constitute our judgment at the time of issue and are subject to change. Neither, the Licensee or any of the Oreana Group of companies, nor their employees or directors give any warranty of accuracy, nor accept any responsibility for errors or omissions in this document. Gordon Thoms and David Conte of Calibre Private Wealth Advisers are Authorised Representatives of Oreana Financial Services Limited ABN 91 607 515 122, an Australian Financial Services Licensee, Registered office at Level 7, 484 St Kilda Road, Melbourne, VIC 3004. This site is designed for Australian residents only. Nothing on this website is an offer or a solicitation of an offer to acquire any products or services, by any person or entity outside of Australia.